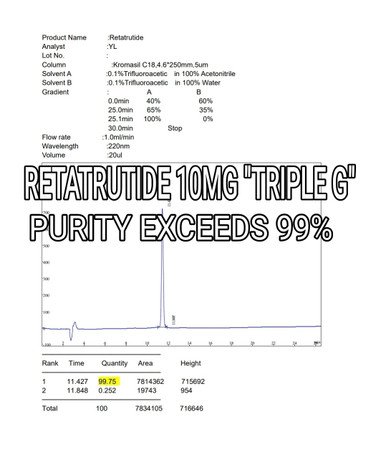
King Retatrutide– World’s 1st Triple Agonist Peptide “Triple G”
“At week 48, a weight reduction of 5% or more, 10% or more, and 15% or more had occurred in a respective 27%, 9%, and 2% of participants who received placebo, compared to 92%, 75%, and 60% of participants who received 4 mg of retatrutide; 100%, 91%, and 75% of participants who received 8 mg; and 100%, 93%, and 83% of participants who received 12 mg.” https://www.pharmacytimes.com/view/retatrutide-treatment-results-in-reductions-in-body-weight-compared-to-placebo
Jastreboff A, Kaplan L, Frías J, et al. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity — A Phase 2 Trial. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(6):514-526. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2301972.
https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/comment/eli-lilly-retatrutide-weight-loss-obesity/
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/995316?form=fpf
Intro:
Over the last few years, scientists have explored innovative approaches to address obesity as a global health challenge. Triple agonist peptides may have potential benefits in the field of weight loss research, a class of compounds with demonstrated efficacy.
Retatrutide (LY3437943) is a triple agonist peptide that activates three specific receptors in the body. Numerous physiological processes are controlled by these receptors, particularly metabolism and appetite regulation. Tri-agonist peptides aim to enhance weight loss outcomes by simultaneously targeting these receptors, resulting in a more comprehensive and synergistic response in the body.
These three receptors are intricately involved in the regulation of energy balance. The first receptor, known as the melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R), is a key player in controlling appetite and energy expenditure. Activation of MC4R has been linked to reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure, making it an attractive target for weight management strategies.
The second receptor, known as the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), is involved in maintaining glucose levels and promoting satiety. Activation of this receptor has been linked to improved insulin sensitivity and a reduced desire for food. As a result, compounds that activate GLP-1R have been investigated for their potential to aid in weight loss by promoting a sense of fullness and reducing overall food intake.
The third receptor targeted by triple agonist peptides is the gastric inhibitory peptide receptor (GIPR), which plays a role in regulating insulin release and lipid metabolism. Activation of GIPR has been associated with improved glucose metabolism and lipid utilization, making it an intriguing target for addressing metabolic dysfunction associated with obesity.
The simultaneous activation of these three receptors by the triple agonist peptide is believed to have a unique and potentially more powerful effect on weight regulation compared to single or dual-receptor agonists. In preclinical studies, animals treated with triple agonist peptides have shown significant reductions in body weight, improvements in metabolic parameters, and changes in food intake patterns compared to control groups.
One of the potential advantages of triple agonist peptides like Retatrutide is their multifaceted approach to weight management. By targeting multiple receptors involved in appetite regulation, energy expenditure, and metabolic function, these peptides aim to address the complex nature of obesity. This comprehensive approach may be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle with traditional weight loss interventions.
Furthermore, the potential benefits of triple agonist peptides extend beyond weight management. These peptides have the potential to improve overall metabolic health and address underlying metabolic dysfunctions associated with obesity.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.